Urban
 Urban areas are already experiencing impacts of a changing climate including increased temperatures, flooding, and extreme storms. These impacts are projected to increase in frequency and magnitude over the next century, leading many cities to develop plans to adapt and prepare for these challenges. Agriculture and forestry sectors can both work to address these changes in an urban environment.
Urban areas are already experiencing impacts of a changing climate including increased temperatures, flooding, and extreme storms. These impacts are projected to increase in frequency and magnitude over the next century, leading many cities to develop plans to adapt and prepare for these challenges. Agriculture and forestry sectors can both work to address these changes in an urban environment.
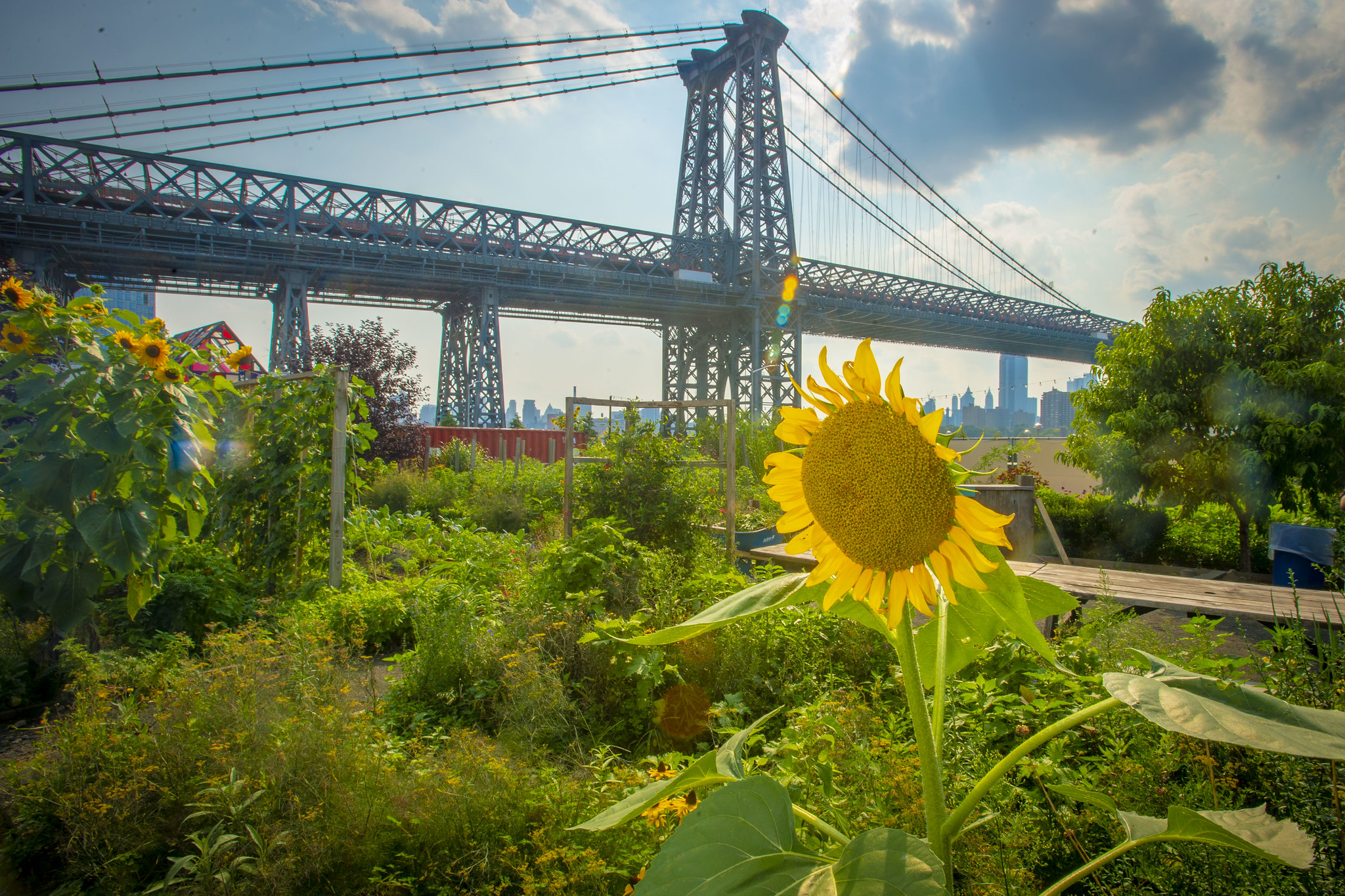
Urban agriculture helps to address local food insecurity issues in cities and suburban areas. Growing food in cities can take the form of backyard, roof-top and balcony gardening, community gardening in vacant lots and parks (sometimes spanning several city blocks), roadside urban fringe agriculture, livestock grazing in open space and intensive indoor hydroponic or aquaculture facilities. Urban agriculture eases access to food, reconnects communities to the practice of growing food, and engages the community on a variety of levels. Increasing tree canopy is often considered in urban climate change adaptation plans, where trees can help reduce local heat island effects, control storm water, and improve air quality. Although urban trees can be an important part of adaptation solutions, they also can be vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. These urban trees may be experiencing stress from improper planting, restricted rooting conditions, road salt, and air pollution already, and therefore extremely vulnerable to climate change.
Browse related content:
-
Specialty Animals
The challenges facing specialty livestock are similar to what is experienced by larger livestock (swine, cattle): the…
-
Growing Seasons in a Changing Climate
The frost-free season length, defined as the period between the last occurrence of 32°F in the spring and the first…
-
Worcester's Urban Forest
Rebuilding Worcester's urban forest with the community after an Asian Longhorned Beetle infestation.
-
Building Resiliency at the Rockaways
The U.S. Forest Service is building stewardship on the Rockaways Peninsula in New York City. By using urban forestry…
-
Demonstration Projects
Demonstration projects are real-world examples of how managers have integrated climate considerations into forest…